If you’ve stumbled across whispered videos, tapping sounds, or oddly satisfying roleplays online, you’ve likely encountered ASMR. But what does ASMR mean—and why does it leave millions of people feeling blissfully relaxed? Let’s unpack the phenomenon, from its quirky origins to its brain-tingling science.
Defined: Breaking Down the Acronym
ASMR stands for Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response, a term coined in 2010 to describe the calming, tingling sensation that starts at the scalp and travels down the spine. Often triggered by specific sights, sounds, or actions, feels like a warm, fizzy wave of relaxation. Common triggers include:
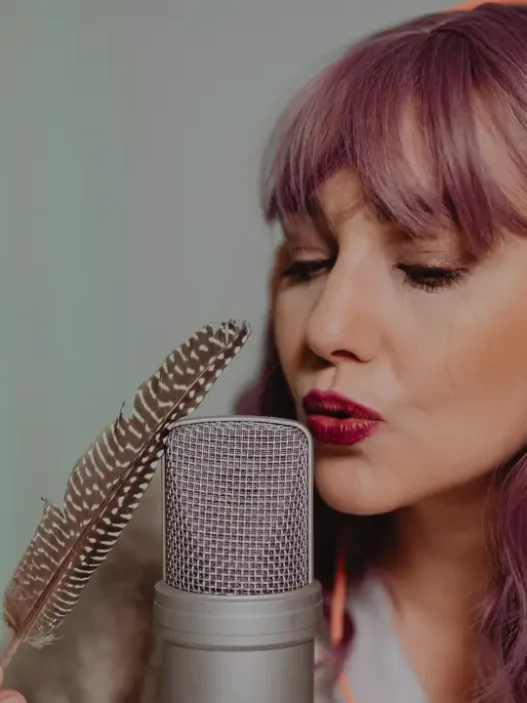
- Whispering or soft-spoken voices
- Gentle tapping or scratching
- Repetitive tasks (e.g., folding clothes, brushing hair)
- Crisp sounds like page-turning or rain
What Does ASMR Feel Like?
Imagine someone lightly tracing patterns on your back, or the quiet hum of a library—ASMR evokes that same soothing, almost hypnotic comfort. Fans describe it as:
- Brain tingles
- A static-like warmth
- Instant stress relief
- A meditative state
Not everyone experiences ASMR (about 20% of people don’t feel it), but for those who do, it’s a powerful tool for unwinding.
Why Do People Watch ASMR Videos?
ASMR isn’t just a quirky trend—it’s a global wellness movement. Popular on YouTube (with billions of views) and TikTok, content helps people:
- Sleep better: Whispered stories or ambient sounds combat insomnia.
- Reduce anxiety: Focused triggers distract from racing thoughts.
- Feel connected: Roleplays (like a virtual spa visit) mimic personal attention.
The Science Behind the Tingles
While research is still evolving, studies suggest ASMR activates brain regions linked to:
- Emotional bonding (e.g., the release of oxytocin).
- Relaxation (lowered heart rate and cortisol levels).
- Sensory focus (heightened attention to repetitive stimuli).
A 2018 study in PLOS ONE found ASMR viewers reported reduced stress and improved mood, validating its therapeutic potential.
Common Misconceptions About ASMR
- “It’s weird or sexual”: Most creators focus on wholesome, non-sexual triggers.
- “Only certain sounds work”: Triggers vary—some love crinkling paper, others prefer silence with hand movements.
- “It’s a placebo”: Brain scans show unique neural activity during ASMR experiences.
Try It Yourself: Popular ASMR Triggers
Curious? Dip your toes into ASMR with these classics:
- Whispered rambles: Check out creators like ASMR Maddy.
- Tapping: Try metal combs, wooden blocks, or even pumpkins (yes, really).
- Visual triggers: Watch someone fold towels or arrange crystals methodical
FAQs About ASMR
Q: Is ASMR linked to synesthesia?
A: Some overlap exists, but they’re distinct—ASMR is about relaxation, not sensory blending.
Q: Can ASMR replace meditation?
A: For many, yes! It offers similar mindfulness benefits without the “quiet mind” pressure.
Q: Why do some people hate ASMR?
A: Misophonia (sound sensitivity) or unfamiliarity can make triggers irritating instead of soothing.
ASMR is a fascinating blend of neuroscience, culture, and self-care. Whether you’re a tingle enthusiast or skeptic, its rise highlights our universal need for calm in a chaotic world. Next time you’re stressed, you might just find solace in the sound of someone tapping a microphone.
Have you experienced ASMR? Share your story in the comments!